In today’s digital landscape, businesses must ensure that their applications and systems work seamlessly together to meet their goals. An enterprise service bus (ESB) is a software architecture that enables organizations to integrate disparate applications and systems, streamlining their business processes and increasing efficiency.
This article will provide a overview of what an ESB is, its role in integration, and its benefits, including examples of how ESBs are used in the real world.
What is an ESB?
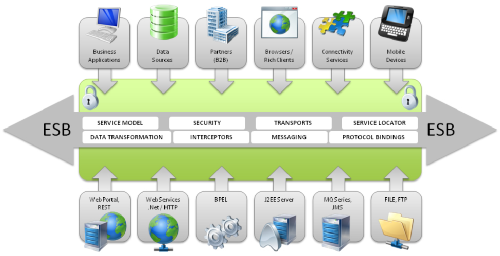
An enterprise service bus (ESB) is a middleware architecture that enables the communication between different applications and systems, regardless of the platforms or technologies used to develop them.
The ESB acts as a messaging system that facilitates the exchange of data and messages between various applications and systems, providing a centralized hub for communication.
The ESB is built using a combination of technologies such as messaging systems, web services, and data transformation tools. These components work together to provide a reliable, secure, scalable communication framework supporting various integration scenarios.
ESB, or Enterprise Service Bus, is a software architecture that enables the integration of disparate systems and applications within an organization
Role of ESB in Integration
The primary role of an ESB is to facilitate the integration of different applications and systems by providing a centralized hub for communication. An ESB allows applications to connect and talk with each other, even if they are working and running on different platforms or using different technologies. This facilitates the exchange of data and messages between different systems, enabling organizations to streamline their business processes and improve efficiency.
ESBs act as a mediator between different applications, handling the routing and transformation of data between different systems. The ESB also provides security and monitoring capabilities, ensuring that data is transferred securely and that organizations can monitor their systems’ performance and behavior.
Benefits of ESB
ESBs offer several benefits to organizations, including:
Improved Connectivity
An ESB enables organizations to connect and communicate with different systems and applications, regardless of the platforms or technologies used to develop them. This improves connectivity and enables organizations to seamlessly exchange data and messages between different systems.
For example, a healthcare organization may have multiple systems, such as electronic health records (EHRs), billing systems, and appointment booking systems. An ESB can help integrate these systems, allowing the healthcare organization to streamline its business processes and improve patient care.
Reduced Complexity
An ESB simplifies the integration process and reduces the complexity of managing multiple systems and applications. An ESB acts as a central hub for communication, providing a familiar interface for different approaches to interact with each other.
For example, a retail organization may have multiple systems, such as inventory management, point-of-sale (POS) systems, and online stores. An ESB can help integrate these systems, enabling the retail organization to streamline operations and improve customer satisfaction.
Increased Agility
An ESB provides a flexible and scalable infrastructure that can quickly adapt to changing all the business needs. An ESB enables organizations to respond rapidly to market changes, allowing them to innovate and remain competitive. With an ESB, organizations can scale their infrastructure up or down as needed, making it easier to support business growth and changing demands.
For example, a financial organization may have multiple systems, such as payment processing systems, customer relationship management (CRM) systems, and fraud detection systems. An ESB can help integrate these systems, enabling the financial organization to respond quickly to changes in the economic landscape and meet its business goals.
Improved Security
An ESB provides a secure communication framework to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access. An ESB provides security features such as message encryption, message validation, and authentication, ensuring that data is transferred securely.
For example, a government organization may have multiple systems, such as tax, law enforcement, and immigration systems. An ESB can help integrate these systems, ensuring that sensitive data is transferred securely and that the organization can protect citizens’ privacy.
Reduced costs: An ESB can help organizations reduce integration costs by reducing the need for custom integration code and providing a standardized approach to integration.
Conclusion
In summary, an enterprise service bus (ESB) is critical to integration. It enables organizations to build a flexible and scalable IT infrastructure outsourcing to streamline business processes, improve efficiency, and reduce costs. By providing a centralized hub for communication between different applications and systems, ESBs can connect various systems and applications, allowing them to exchange data and messages seamlessly.
ESBs offer several benefits, including improved connectivity, reduced complexity, increased agility, and improved security. ESBs are used in various industries, such as healthcare, retail, finance, and government, to streamline operations and meet business goals.
Overall, ESBs are a crucial component of modern IT infrastructures outsourcing, enabling organizations to stay competitive in today’s digital landscape.
Overall, an ESB can help organizations improve their agility, scalability, data integration, security, and reduce complexity and costs associated with managing integrations.