Agriculture is the primary source of the economy; it includes intensive functioning and utilization of soil and groundwater. Greenhouse emissions from agriculture are a significant source of climate change and the greenhouse effect. However, the effects of climate change on agriculture are far-reaching and could pose a future threat to food security.
The climate has a big impact on agriculture. In some regions, rising temperatures and levels of carbon dioxide may improve crop yields. The availability of water, soil moisture, nutritional levels, and other factors must also be satisfied to reap these benefits.
Food safety may be threatened by changes in climate, causing droughts and floods, which could present difficulties for farmers and ranchers.
Understanding the Effects of Climate Change on Agriculture
Agriculture is regarded as the food feeder to the large population around the globe. However, it is a well-known fact that farming is also a very large contributor to global warming and there is the various effect of climate change on agriculture. This includes the rapid expansion of farming land area which causes deforestation.
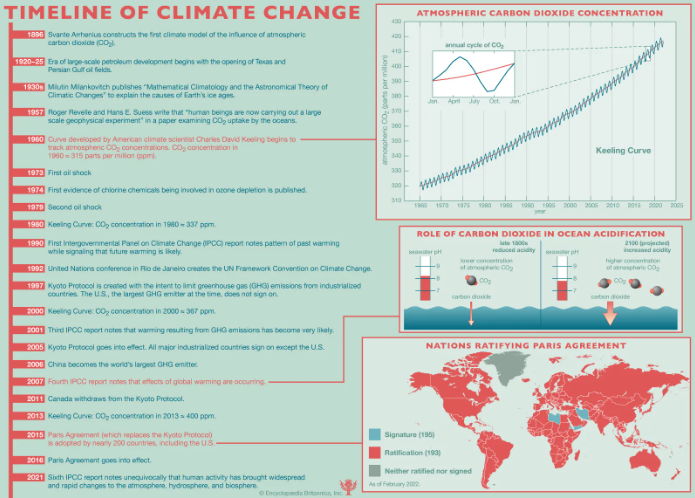
The effects of climate change on agriculture can cause severe effects on world food security. It is needed to be understood in a broader sense, that due to climatic change many species of plants and trees will stop growing and go extinct.
The Implication of The Agriculture Sector
Both agriculture and climate change are global phenomena that interact with one another. Numerous factors, such as variations in insects and diseases, variations in atmospheric co2 and surface ozone concentrations, variations in the nutritional value of some foods, variations in sea level, and variations in rainfall, mean temperature, average extreme climatic condition (such as heat waves), all have an impact on farming.
Agriculture is already being impacted by climate change, albeit the effects are unevenly spread worldwide. Crop output in low latitude nations will likely be negatively impacted by future climate change, whereas northern latitude impacts could be either beneficial or negative.
For some sensitive groups, like the poor, climate change will likely raise the risk of food shortages. It may affect underdeveloped countries of Africa where there is already a situation of food shortage.
Factors Affection Agriculture Sector Due to Climate Change:
By emitting greenhouse gases (GHGs) and converting non-farmland (like forests) into farmland, agriculture contributes to global climate change. Around 20 to 25 percent of the world’s yearly emissions in 2010 came from agriculture, forestry, and changes in land use.
- Annual rise in sea level
- Frequent floods in the low-laying area
- Crop failure due to global warming
- Natural calamities such as earthquake
- Loss of humus causing drought.
These are some of the factors which result in lower productivity in agricultural sectors due to climate change. This can lead to loss of crop productivity and crop failure resulting in rising food prices and even famine in poor countries.
Response To the Global Market
The food that is produced, processed, packed stored, delivered, prepared, and served before it reaches our plates. Food supply emits greenhouse gases (GHGs) into the atmosphere at every stage. Nitrous oxide and methane, two potent greenhouse gases, are released in exceptionally large amounts by agriculture.
Livestock create methane during digestion as a result of enteric fermentation, which is then expelled by belching. Additionally, it may escape from landfills’ organic waste and manure storage. Mineral and organic nitrogen fertilizers are a secondary source of nitrous oxide emissions.
How Can Sustainable Practices Control in the Effects of Climate Change on Agriculture?
The agricultural sector needs a reform that could be more eco-friendly and have and alter the effects of climate change. The above article it is discussed the necessity of the eco-agricultural sector. This firm provides consultation regarding sustainable and smart farming that impacts less on climate. This is how we can encourage suitability in the agricultural sector of the economy.





